Categories
Tags
457 words
2 minutes
Auth LDAP Kerberos
Auth LDAP Kerberos
Protocols Used in Active Directory
| Protocol | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Kerberos | Default authentication protocol for domain accounts. Provides secure, ticket-based mutual authentication. |
| DNS (Domain Name System) | Used for name resolution; critical for locating domain controllers and other AD services. |
| LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) | Used to query and modify items in Active Directory, such as user and group information. |
| MSRPC (Microsoft Remote Procedure Call) | Used for communication between AD-related services (client-server interaction). |
Kerberos
- Kerberos is the default authentication protocol for domain accounts in Windows since Windows 2000. It is a ticket-based, stateless, and mutual authentication protocol used to authenticate users and services securely.
Key Components:
- KDC (Key Distribution Center): Runs on Domain Controllers, consisting of two parts:
- AS (Authentication Service)
- TGS (Ticket Granting Service)
- TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket): Issued after user login and used to request service tickets.
- TGS Ticket: Grants access to specific services.
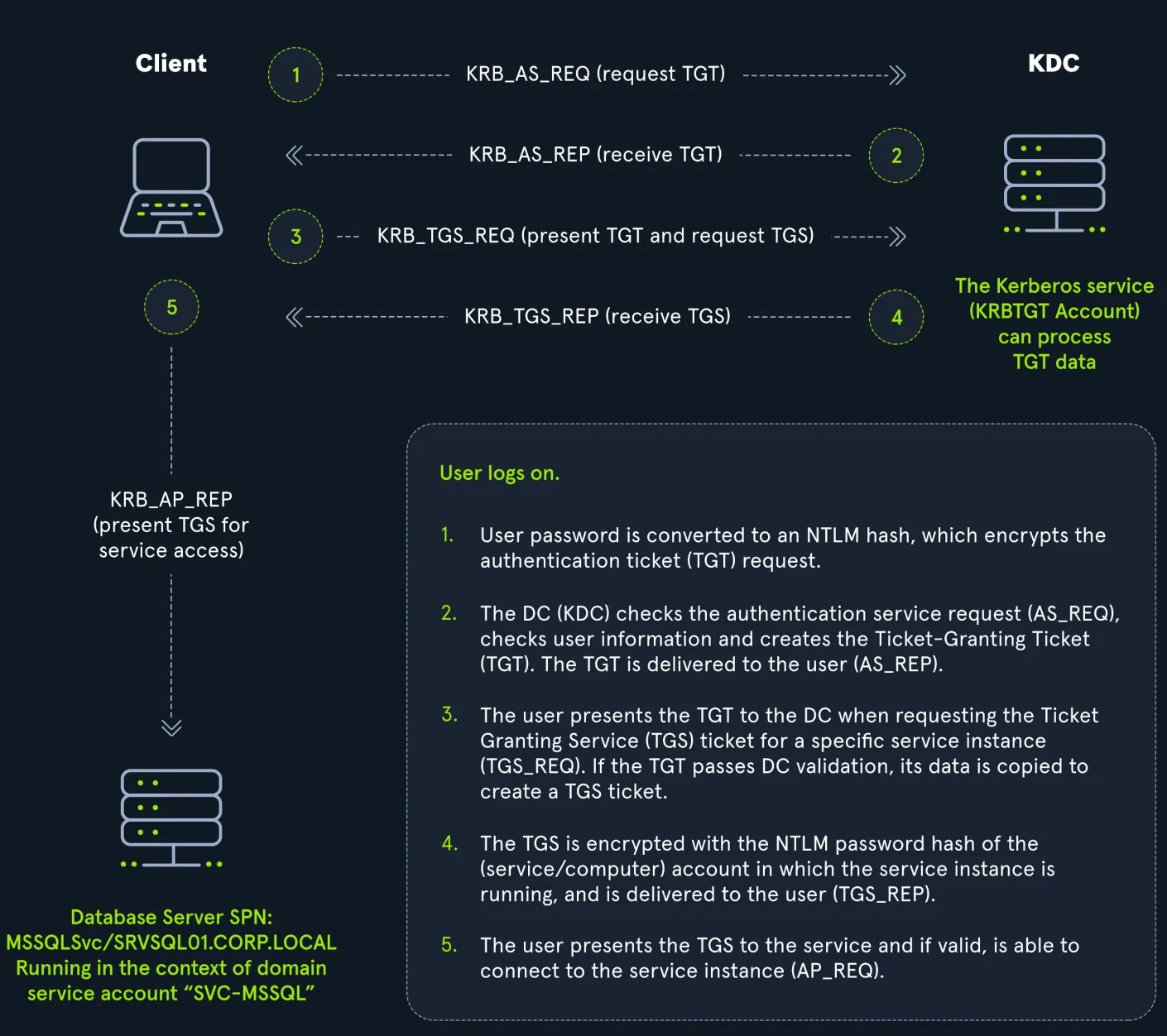
Authentication Flow:
- AS-REQ: User logs in → password encrypts timestamp → sent to KDC.
- AS-REP: KDC verifies → sends TGT back encrypted with
krbtgtsecret key. - TGS-REQ: TGT presented to KDC to request access to a service.
- TGS-REP: KDC issues TGS ticket, encrypted with the NTLM hash of the service.
- AP-REQ: Client presents the TGS to the service → if valid, access is granted.
Ports:
- Uses Port 88 (TCP/UDP)
Benefits:
- No passwords transmitted over the network.
- Stateless design means no tracking of previous requests.
- Integrated tightly into Active Directory (AD).
DNS (Domain Name System)
- DNS is essential in Active Directory environments for name resolution and locating Domain Controllers (DCs).

Functions in AD:
- Resolves hostnames to IPs (forward lookup).
- Resolves IPs to hostnames (reverse lookup).
- Uses SRV records to allow clients to find services like file servers, printers, DCs, etc.
- Dynamic DNS automatically updates records, reducing manual errors.
Example Commands:
# Forward Lookup
nslookup INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL
# Reverse Lookup
nslookup 172.16.6.5
# Lookup host IP
nslookup ACADEMY-EA-DC01Ports:
- Port 53 (TCP/UDP)
- UDP is default, falls back to TCP if necessary (e.g., large queries >512 bytes)
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
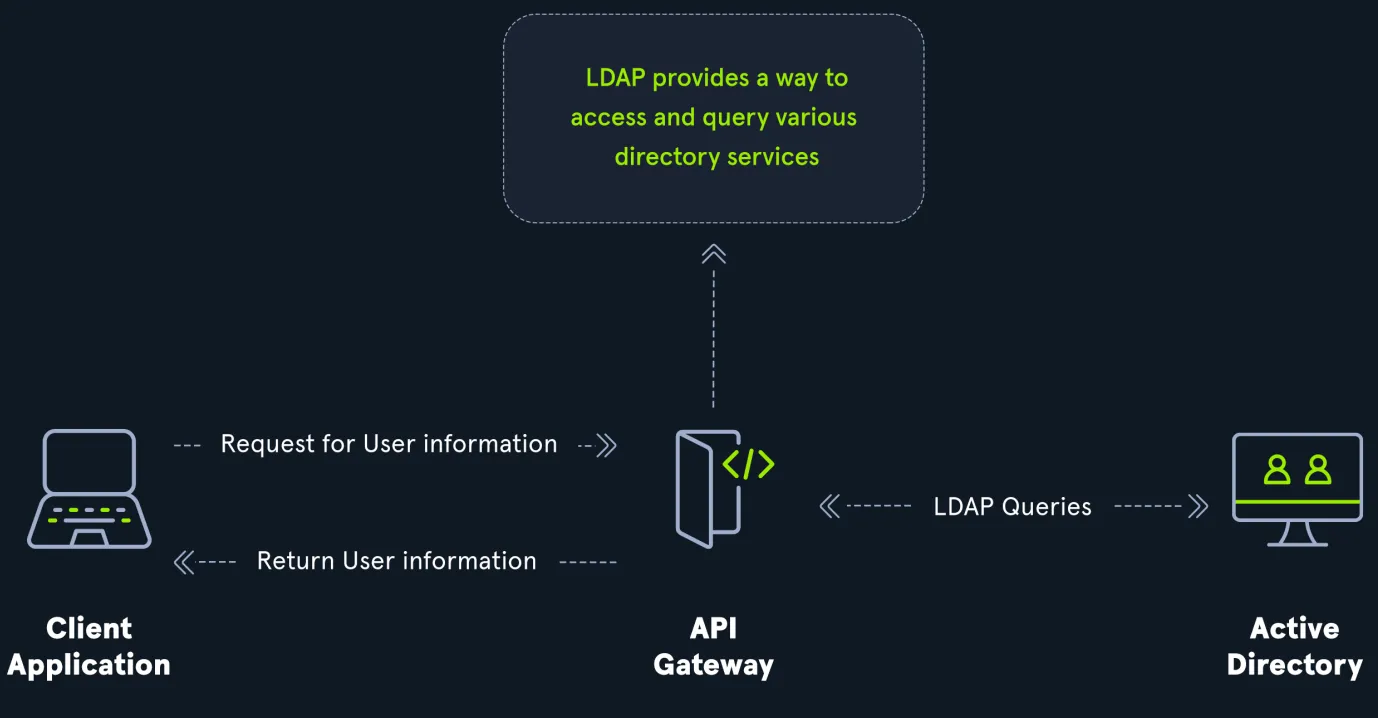
LDAP is an open protocol used for querying and modifying items in directory services, particularly Active Directory.
Ports:
- LDAP: Port 389
- LDAPS (Secure LDAP): Port 636
Usage in AD:
- Used to authenticate users and manage directory information.
- Handles searches, modifications, and access control within AD.
Authentication Types:
- Simple Authentication:
- Username + Password in plaintext.
- Includes anonymous and unauthenticated binds.
- SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer):
- Uses mechanisms like Kerberos for secure binding.
- Includes a challenge-response process for secure verification.
Security:
- Unencrypted by default – vulnerable to sniffing.
- Use TLS or LDAPS for secure communication.
MSRPC (Microsoft Remote Procedure Call)
- MSRPC is Microsoft’s version of RPC used for interprocess communication between services in Windows.
Key Interfaces:
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| lsarpc | Interfaces with the Local Security Authority (LSA); manages security policies and interactive logins. |
| netlogon | Authenticates users and services; critical for domain-based logins. |
| samr | Provides remote access to the Security Account Manager (SAM); used to manage user/group accounts. |
| drsuapi | Handles directory replication between DCs; used by attackers to dump NTDS.dit (AD database). |
Security Implications:
- samr: By default, allows all authenticated users to query domain user info.
- drsuapi: Used in attacks like DCSync to replicate the AD database and extract password hashes.
Auth LDAP Kerberos
https://fuwari.vercel.app/posts/active-directory/auth-ldap-kerberos/